
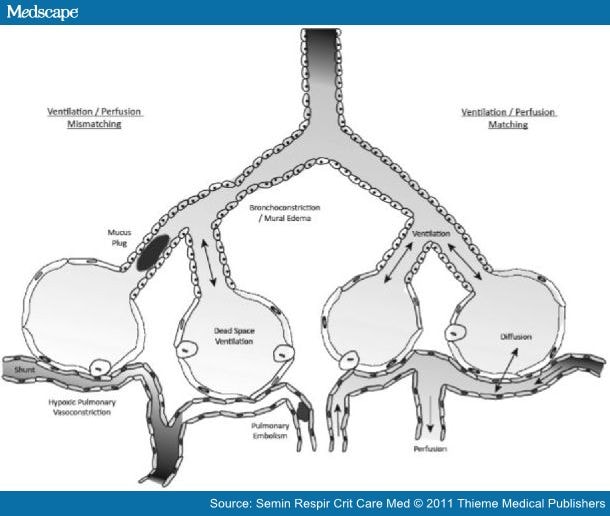
Ventilation (V) refers to the flow of air into and out of the alveoli, while perfusion (Q) refers to the flow of blood to alveolar capillaries.

For effective gas exchange to occur, alveoli must be ventilated and perfused. Gas exchange occurs in the lungs between alveolar air and the blood of the pulmonary capillaries. Most bronchioles and large airways are part of the conducting zone of the lung, which delivers gas to sites of gas exchange in alveoli. The lungs are composed of branching airways that terminate in respiratory bronchioles and alveoli, which participate in gas exchange. One of the major roles of the lungs is to facilitate gas exchange between the circulatory system and the external environment.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
